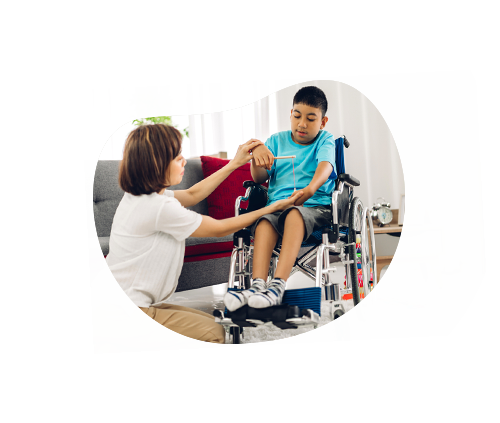





Speech therapy is a form of treatment for speech and language disorders, which include issues with word and sound production. Language disorders refer to problems understanding sounds, words, and sentences, as opposed to problems understanding words and putting sentences and ideas together for communication. Speech therapy aids children in developing their speech and communication skills. Speech therapists can prescribe repetitive exercises as well as communication aids as part of what is considered speech therapy. These tools, often known as augmented and assisted communication (AAC) enable speech or sound production for those who are nonverbal.
It is the primary focus of a speech-language pathologist to treat children as well as adults with communication disorders such as speech disorders, problems with written language, and voice disorders such as stuttering and stammering, among others. The problems of the children are evaluated by the speech therapist who also offers immediate treatment. 1. Children with speech disorders could have trouble pronouncing sounds. 2. A rough voice 3. Stammering or repeating sounds. Understanding, taking, reading, and writing may all be problematic for children with language issues.
Development in Personal, Social, and Emotional Areas:
Personal, social, and emotional development examines how children become self-assured and self-reliant, as well as how they make decisions. Children who struggle with language and communication may find it difficult to articulate their wants and preferences, which prevent them from making their own decisions. The process of playing and interacting with children is essential for the growth of excellent interpersonal skills. In social situations when they find it challenging to interact or participate effectively, children may lack confidence, which can severely affect their interpersonal and emotional challenges.
Relationships with friends:
The fostering of friendships depends on children interacting well with one another. They connect with one another and communicate with one another to form friendships. Eye contact, body language, and gestures must be used in conjunction with language in order to effectively communicate. As children grow, language becomes increasingly significant for preserving and building relationships. Children who have trouble talking might not make friends.
Behavior:
Behavior and issues with language and communication are closely related. Children who have trouble hearing and understanding language may not comprehend the rules, boundaries, or environment of the school. The child may express their rage or anger as a result of this since they cannot understand why they are not permitted to do anything. Children who struggle with communication may have fewer opportunities for social connection with other children and less practice collaborating and sharing with others. Children might not comprehend the social norms of play in this situation, leading to the child stealing toys rather than learning how to share. Children who struggle to express themselves verbally could become frustrated if they are unable to articulate their wants and requirements.
Play:
Children benefit from play. The Early Years Foundation Stage curriculum emphasizes play as a valuable way for children to learn. Play is crucial for children's development, helping them gain confidence as they discover the world, solve issues, and interact with others. Children who struggle with communication may find it challenging to communicate with and relate to other children while playing. As they get older, children like to play games with rules in teams and communicate using language. Children get isolated and excluded from other children's activities if they have trouble interacting with others or comprehending the rules of the games. Their self-esteem and confidence are also affected by this.
Literacy:
Children's reading development is mostly dependent on their speech and language abilities. Delays in the acquisition of reading and phonic abilities might be caused by problems interpreting and processing language. Understanding written communication is a crucial skill for learning because it aids learning in many subject areas.
Mathematics:
Numerical learning often involves the ability to understand the language and instructions in order to solve problems and reason. Numerous other branches of mathematics also use mathematical languages, such as names for numbers, shapes, and numerical expressions. Mathematical delays in children with communication issues can result from the intimate relationship between reading and mathematics.
Language activities:
Activities that encourage language development include playing and chatting, incorporating images from books, objects, current events, etc. To improve speech and language abilities, therapists may also utilize repetition exercises and model proper pronunciation.
Articulation therapy:
Articulation therapy involves having the therapist role-play the proper sounds and syllables for children, frequently while engaging in play activities. All activities have to be both age-appropriate and pertinent to the particular therapeutic requirements of children. The speech-language pathologists may physically demonstrate how to move children's tongues to make particular sounds, such as the "r" or "t" sound, to children. In this exercise, a mirror may occasionally be used.
The oral-motor aspect of feeding and swallowing therapy:
Children can expect their speech-language pathologists to recommend a variety of oral exercises, including various tongues, lip, and jaw exercises to strengthen the muscles of the mouth if eating or swallowing is difficult. The speech-language pathologists may also use various food temperatures and textures to improve children's oral awareness while they are eating and swallowing.
Recommendations and follow-up expectations:
The speech therapist will go over their professional conclusions with the children and offer suggestions for the length and duration of the speech. They can be seeking advice, tools, and information about how to work with children in between treatment sessions if the therapist does not offer homework. Observe this as a parent. The greatest teacher of children is their parents. Children’s speech and language development are more likely to improve the more parents help their therapist provide consistent therapy activities.
It helps children with coordination problems or palate problems who have difficulty communicating. The child must make words and noises. The most effective way to help the child is speech therapy. Other life skills are built upon the foundation of communication. There is not much opportunity for success in the classroom, in forming and maintaining relationships, in literacy, or in learning when communication is hampered. Children who are unable to speak have a hard time understanding what is being taught in the classroom and are unable to engage in class discussions. This results in the children not succeeding in their assignments and giving others the impression that they are slow and ignorant. This is a difficulty that older individuals with declining hearing and vision experience. Their worlds are so limited that they mistakenly think they are old while, in reality, they are only unable to respond appropriately due to poor information. If communication disorders were identified and addressed while they were young, many adult communication issues might be lessened or assisted.
Speech therapy boosts self-esteem for children who have speech impairments and are aware of it. Children who speak differently from other children are aware of this, which can severely lower their self-esteem. Speech-language treatment, for instance, significantly boosts children's self-confidence when it comes to traditional concerns like lisping, changing Rs into Ws, and stuttering. These issues could be cute when children are five years old, but not when they are ten.
Children may be enrolled in speech therapy if they appear to be struggling socially at school and it is apparent that they have a speech problem. Confidence grows as communication improves. Their speech will soon improve as a result of learning new speech techniques.
Speech therapy increases: Educational success and self-esteem, give children the means they need to deal with their speech problems for the rest of their lives.
Capacity to retain new skills acquired: Speech therapy for children who only makes a few minor mistakes (one or two wrong sounds) usually takes one academic year to complete. Many mistakes may require extra time to fix. Finally, the children select appropriate goals that support their holistic development and boost social skills, communication across the board, and the ability to operate in daily life.
Enhances Social Skills: Sociable and practical abilities are necessary to interact with others in one's society and daily life. Practical language abilities are frequently severely delayed and disorganized when children have limited or nonexistent functional speech. Video modeling, role-playing, specialized therapy applications, sociable storytelling, and other techniques and technologies can all be used to target social skills. It is crucial to combine these tactics for social skill improvement with the usage of supported communication.
Aids in Reading: Communication can benefit substantially from literacy and reading abilities. Children communicate freely when they spell words. The secret to effective interpersonal communication may lie in teaching these fundamental abilities.
Improves Alternative Communication Techniques: Work on additional communication techniques to help with communication, such as vocalizations, gestures, sign language, approximations, and other means. Individuals use a comprehensive approach to communicating. Speech, writing, typing, eye contact, gestures, facial expressions, and many other types of communication are all ways that are meant to communicate including educating children on how to interact informally and in different ways, such as using the signs for "bathroom," "food," and "drink," tapping someone on the shoulder to gain their attention, etc. Additionally, if children repeatedly make certain sounds, give them meaning. If they say "ha," for instance, that is substituted instead of "help." Children substitute "ba" for "book" if that is relevant to the particular person in question.
Decreases frustration with communication: Children who receive speech therapy are able to communicate better with adults and other children. The exercises focus on strengthening the speaking muscles. Speech therapy exercises entail mimicking the speech therapist and repeating sounds.
Sign language and hand gestures: Speech therapists have long employed sign language to foster communication, despite the fact that it is typically thought of as the language of the hard of hearing. Common nonverbal cues like pointing and head movements are easily recognized. So until the child is able to speak, employing a formal system of gestures in place of spoken words is a worthwhile approach. Children are able to communicate more efficiently with this method.
Picture Exchange Communication System/Picture Communication Symbols (PCS): Children with limited or no communication skills can use image symbols to communicate. With the appropriate picture cards, children can communicate or think. PCS starts off with the exchange of basic icons but quickly develops sentence structure to produce a self-initiating, useful communication system.
VOCA (voice output communication aids): Children may electronically "talk" thanks to VOCA, an electronic speech-generating gadget. It could be computer-generated speech that has been synthesized, pre-recorded speech, or both. These aids can be used in a variety of ways. Children can, for instance, make requests and submit ideas by flipping a switch, pressing buttons, using a touchscreen, or using a keypad. The corresponding words are then spoken by the device.
Dental motor interventions: The way tongue, lips, cheeks, and jaw muscles are used is dependent on oral motor power. Oral motor therapies are activities that help children gain awareness, mobility, strength, coordination, and flexibility so they can talk. Speech therapists assist children with language or communication challenges by extending their repertoire of communication strategies. These strategies can range from low-tech ones like drawings, gestures, and verbal exercises to high-tech ones like speech-generating gadgets. Children can learn to utilize some or all of these techniques to comprehend what others are saying, express their needs, offer remarks, and respond to others' inquiries.
Usage of Core Boards: When working with Core Boards, children are exposed to the language and basic terminology. Core boards can be used to increase engagement while modeling language. When used in conjunction with activity-specific words, they can aid children in developing their capacity for activities like reading books and improved communication.
We give our learners a better knowledge of how various disabilities affect a child's life. We examine the history of special education and the major challenges they confront through parent support. As a result, learners become a part of one of the top online special education programs available here.
From the comfort of their homes across the globe, we offer learners expert instruction from special educators. Learners also benefit best through our personalized education plans and techniques that use international education methodologies that help students grow in a way that suits their abilities.